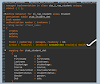
The READ operation in ABAP RAP (RESTful Application Programming Model) is a unique and powerful mechanism, distinctly different from traditional ABAP READ TABLE or SELECT statements. It enables reading transactional data from the buffer, supports granular filtering, and incorporates additional control parameters for precise data fetching.
Let’s dive into how READ works in RAP and why it’s essential for building robust SAP Fiori applications.
Key Differences Between RAP READ and ABAP READ
1️⃣ Transactional Buffer Access:
RAP READ operations are performed on the transactional buffer, allowing access to data that may not yet be persisted to the database.
2️⃣ Special Parameters:
RAP introduces special parameters like %key, %control, %tkey, and others. These parameters serve to control the filtering and field selection logic dynamically.
3️⃣ Dual Result Tables:
Unlike traditional reads, RAP provides separate tables for successful and failed read operations:
-
RESULT: Holds records successfully fetched. -
FAILED: Contains entries where the read failed (e.g., due to missing or incorrect key values).
Step-by-Step: How RAP READ Works
Step 1: Use the FROM VALUE Clause
The READ statement leverages FROM VALUE to pass in a table of filter conditions (similar to a WHERE clause).
Step 2: Specify %key and %control Parameters
-
%key: Used to specify key fields for the entity (e.g.,
travelid). -
%control: Indicates which fields should be read from the selected record(s).
For single record validation, use the interfaceif_abap_behv=>mk-onto mark fields as “on”.
Step 3: Handle Multiple Key Fields
If the CDS entity has multiple key fields, ensure that all key fields are provided in the %key structure.
Step 4: Process Results and Failures
Once the READ is executed:
-
RESULT Table: Contains successfully fetched records.
-
FAILED Table: Contains entries where the read failed (e.g., invalid keys, missing entries).
You can handle both tables in your logic to process valid records and manage errors effectively.
Advantages of RAP READ
✅ Access Uncommitted Changes: Read data from the buffer before database commit.
✅ Dynamic Field Selection: Use %control to fetch only necessary fields, improving performance.
✅ Error Handling: Distinct RESULT and FAILED tables enable clean error management.
✅ Granular Filtering: Supports precise data filtering using FROM VALUE.
✅ Consistency in Multi-User Scenarios: Ensures accurate and consistent data handling during transactional operations.