Creating a Managed RAP (RESTful Application Programming) Project involves several structured steps. Here’s a streamlined guide:
Steps to Create a Managed RAP Project:
Create a Custom Table
- Ensure the key field is auto-incremented and dynamically generated.
- Key fields should always be not null to maintain data consistency.
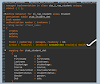
Create a Root Interface Entity View
- This basic view sits on top of the custom table.
- Used in EML (Entity Manipulation Language) statements for handling CRUD operations.
- Associations, compositions, and calculations are performed at this level.
Create a Root Projection/Consumption View
- Built on top of the root interface view.
- Displays all fields from the interface view and its associations.
- Element-level annotations help distinguish projection views based on operations.
Create a Metadata Extension File
- Defines UI elements such as line positions, facts, search helps, identification, and user actions.
- All fields in metadata extensions must have annotations.
Create Behavior Definitions
- Required for both root interface view and root projection view.
- The behavior definition on the interface view must include implementation classes and mapping to connect the table and interface view.
Create a Service Definition
- Exposes consumption views.
- All views connected via associations and compositions must be exposed; otherwise, respective projections won’t be available after publishing.
Create a Service Binding & Publish the Project
- The final step is to bind the service and publish the exposed projection.
- The final step is to bind the service and publish the exposed projection.