Custom RAP (RESTful ABAP Programming) tables allow developers to tailor their data structures to specific business needs. Here's a structured guide to creating a custom table and implementing a class to generate data for it.
Step 1: Creating a Custom Table
Selecting Fields & Table Creation
- Identify Required Fields – Review the standard table and select the relevant fields needed for customization.
- List the Chosen Fields – Document the required fields to ensure consistency and accuracy in table creation.
- Create a New Custom Table – Use the development environment to define the new table.
- Add Selected Fields to the Custom Table – Incorporate all identified fields from the standard table to maintain data integrity.
Developing a RAP-Compatible Class
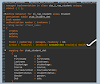
- Create a Standard Class – Open your development environment and define a new class.
- Utilize the Standard Interface – In the public section of the class definition, declare
if_oo_adt_classrunto leverage predefined functionalities. - Implement the Main Method – Define
if_oo_adt_classrun~mainto execute the core logic. - Insert Business Logic – Integrate the required logic, as outlined in reference documentation or screenshots, within the main method.
- Execute & Validate – Run the method (
F9) to confirm correct functionality and data generation in the custom RAP table.
Final Thoughts
Creating a custom RAP table enhances data management and ensures structured processing. By following these steps, developers can streamline custom table creation and data generation, optimizing business applications efficiently